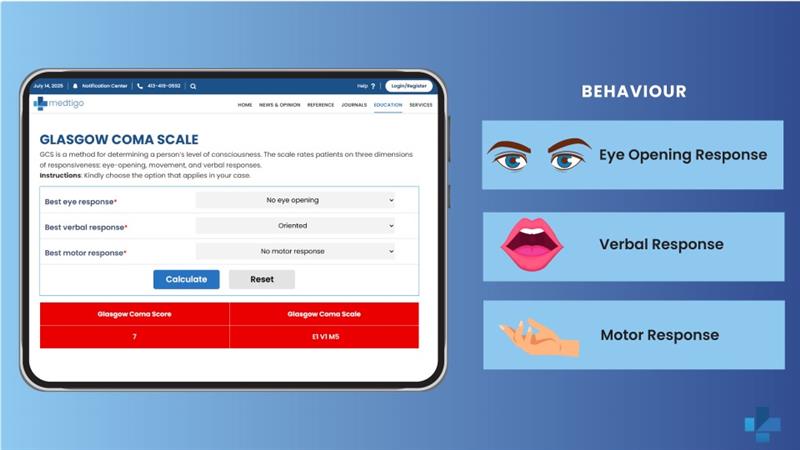
Healthcare professionals assess the level of consciousness in patients by using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) as a standard tool. In emergency and neurological situations, this scale is specifically used to make quick decisions and provides clinicians with accurate results for evaluating brain function, helping guide future treatment.
medtigo provides a free online GCS calculator that is more accessible and provides a fast and precise assessment at the point of care.
Try the GCS Calculator for free on medtigo with quick and accurate assessments.
The neurosurgeons Graham Teasdale and Bryan Jennett introduced GCS in 1974 to give a reliable measure of the level of consciousness in patients after brain injury.
The GCS is commonly used in conditions like:
- Head trauma
- Stroke
- Altered mental status
- Coma or unresponsiveness
- Postoperative neurological monitoring
Understanding the Three Components of GCS
GCS Score Breakdown
The GCS contains three measurable responses: Eye Opening (E), Verbal Response (V), and Motor Response (M). Each component has a designated score range, and the total score is the sum of these values.
GCS Score Table
Eye Opening (E)
- Spontaneous: 4
- To sound: 3
- To pressure: 2
- None: 1
Verbal Response (V)
- Oriented: 5
- Confused: 4
- Inappropriate words: 3
- Incomprehensible sounds: 2
- None: 1
Motor Response (M)
- Obeys commands: 6
- Localizes pain: 5
- Withdraws from pain: 4
- Abnormal flexion (decorticate): 3
- Abnormal extension (decerebrate): 2
- None: 1
How to Calculate GCS Step-by-Step
How to calculate GCS
To calculate the GCS, add the scores from each of the three components:
GCS = E + V + M
Example Case
A patient opens their eyes to pressure (E2), makes incomprehensible sounds (V2), and localizes pain (M5).
Total GCS = 2 + 2 + 5 = 9
Score Interpretation Range
- Minimum score: 3 (deep unconsciousness)
- Maximum score: 15 (fully alert and responsive)
Clinical Interpretation of GCS Scores
GCS interpretation
GCS Score Categories
- Mild (13 to 15): Patient is conscious, may be disoriented or confused, typically stable.
- Moderate (9 to 12): It suggests a moderate injury. Patients may be confused or lethargic and need observation and possible imaging.
- Severe (3 to 8): It indicates a comatose or unconscious state. An immediate intervention is likely needed, such as airway protection or ICU care.
Why It Matters
GCS interpretation enables the making of clinical decisions regarding the need for intubation, ICU admission, or neurosurgical consultation. It also provides a reliable metric to monitor neurological changes over time.
When and Why to Use the GCS Calculator Tool
GCS calculator online
The GCS Calculator from medtigo helps reduce calculation errors, particularly in high-pressure environments such as trauma bays, ICUs, and ambulances.
Advantages of Using the Tool
- Speeds up the assessment process
- Reduces chances of manual scoring error
- Easy to use on mobile or desktop
Who Should Use the Calculator
- Emergency physicians
- Paramedics and EMTs
- ICU and trauma nurses
- Neurologists
- Medical students and residents
Access the GCS Calculator on medtigo to streamline neurological assessments.
Other Useful Calculators for Emergency or ICU Use
Critical care medical calculators
In addition to the GCS calculator, medtigo gives a comprehensive collection of tools that support quick clinical decision-making:
- CURB-65: Evaluates pneumonia severity
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): Assesses tissue perfusion
- Anion Gap Calculator: Diagnoses metabolic acidosis
- BMI Calculator: Assists with weight-related assessments and dosing
Explore medtigo’s complete Calculator Hub for more critical care tools.
Conclusion
In acute and critical care settings, the GCS tool evaluates brain function. Healthcare practitioners can enhance patient outcomes and clinical efficiency by understanding their components and regularly applying them.
Use medtigo’s free GCS Calculator to speed up and improve the reliability of your evaluations—access medtigo’s comprehensive range of medical calculators designed for real-time, evidence-based decision-making.
Visit medtigo’s Medical Calculator Hub and enhance your clinical workflow with tools you can trust.